Personal finance encompasses the management of your money through budgeting, saving, investing, and planning for your financial future. In today’s complex economic landscape, developing “strong financial literacy“ has become essential for anyone seeking to achieve their short and long-term goals, whether it’s buying a home, funding education, or securing a comfortable retirement.
The fundamentals of personal finance are timeless, yet the tools and strategies available to individuals continue to evolve rapidly. From “mobile banking apps“ to robo-advisors and cryptocurrency, navigating today’s financial landscape requires both traditional wisdom and awareness of emerging opportunities.
Do not save what is left after spending, but spend what is left after saving.
Warren Buffett
Financial literacy remains surprisingly low across the population, with studies showing that only about one-third of adults understand basic concepts like interest compounding, inflation, and risk diversification. This knowledge gap has real consequences: those with stronger financial literacy tend to accumulate more wealth, manage debt better, and experience less financial stress throughout their lives.
Building a Strong Financial Foundation: The Budgeting Fundamentals
Before considering investments or complex financial strategies, establishing a solid foundation through effective budgeting is essential. A well-structured budget serves as the roadmap for all your financial decisions.

The foundation of sound personal finance begins with “informed decision-making” about your cash flow. Understanding exactly where your money comes from and goes each month provides clarity and control that empowers better financial choices.
The 50/30/20 rule offers a simple framework for budgeting that many financial experts recommend. This approach allocates 50% of after-tax income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment, creating balanced financial priorities that can be sustained over time.
Modern budgeting has been revolutionized by technology. Apps like Mint, YNAB (You Need A Budget), and Personal Capital can automatically categorize expenses, track spending patterns, and provide insights that would have required hours of manual calculation in the past. These tools make consistent budget maintenance more accessible to everyone.
Budgeting Best Practices
Research shows that people who maintain detailed budgets save an average of 20% more money than those who don’t track their spending. Setting specific financial goals, reviewing your budget regularly, and building flexibility for unexpected expenses are key practices that significantly improve financial outcomes over time.
Zero-based budgeting, where every dollar is assigned a specific purpose, helps eliminate wasteful spending and ensure your money aligns with your priorities. This approach “minimizes financial leakage” that often occurs when cash flow isn’t carefully monitored and managed.
Emergency Funds: Your Financial Safety Net
An emergency fund is your financial first line of defense against life’s unexpected challenges. This dedicated savings reserve ensures that surprise expenses don’t derail your broader financial plans or force you into debt.

Most financial experts recommend having 3-6 months of essential expenses saved in an easily accessible account. However, your specific circumstances might warrant a larger or smaller fund. Self-employed individuals, those with variable income, or people with dependents often benefit from larger emergency reserves to account for greater financial uncertainty.
Free Download
Download our comprehensive Emergency Fund Calculator to determine exactly how much you should have saved based on your specific circumstances. This free tool helps you analyze your essential expenses, income stability, and family situation to create a personalized emergency savings target that provides true financial security.The location of your emergency fund matters almost as much as its size. These funds should be kept in highly liquid accounts like high-yield savings accounts that offer some return while maintaining immediate accessibility. Avoid volatile investments or accounts with withdrawal penalties or restrictions.
Using “strategic fund building” helps make the process of establishing an emergency reserve more manageable. Start with a modest goal of $1,000, then gradually increase to one month of expenses, and continue building until you reach your target amount. This “incremental approach” makes the process less overwhelming.
Smart Debt Management: Handling Credit Effectively
Understanding how to use credit wisely and manage debt effectively is a crucial component of personal finance. Not all debt is created equal, and knowing the difference between productive and destructive borrowing can significantly impact your financial health.

A strong credit score opens doors to better interest rates and terms on loans, potentially saving you thousands over your lifetime. Maintaining good credit requires consistent on-time payments, keeping credit utilization low (ideally below 30%), and monitoring your credit reports regularly for errors or suspicious activity.
The two most popular debt repayment strategies are the debt snowball and debt avalanche methods. The snowball approach focuses on paying off smallest balances first for psychological wins, while the avalanche method targets highest-interest debts first for maximum mathematical efficiency. Both have merits, and the best choice depends on your personal motivation style.
Refinancing or consolidating high-interest debt can accelerate your path to being debt-free. Options like balance transfer credit cards, personal loans, or home equity lines of credit might offer opportunities to lower interest rates and simplify payments. However, these strategies require “careful consideration” of fees, terms, and your ability to avoid accumulating new debt.
Comparing Debt Repayment Strategies
Understanding the various approaches to debt repayment can help you choose the method that best aligns with your financial situation and personal psychology.
| Debt Snowball | Debt Avalanche | Debt Consolidation | |
| Basic Approach | Pay off smallest balances first | Pay off highest interest rate debts first | Combine multiple debts into a single loan |
| Psychological Benefit | Quick wins build motivation | Minimal; focuses on math efficiency | Simplifies payments and reduces stress |
| Financial Efficiency | Lower; may pay more interest | Higher; minimizes total interest paid | Varies based on new interest rate |
| Best For | Those needing motivation from early successes | Those disciplined about long-term savings | Those overwhelmed by multiple payments |
| Impact on Credit Score | Positive as accounts are paid off | Positive, but slower reduction in number of accounts | Initial small drop, then improvement with on-time payments |
| Time to Debt-Free | Mathematically longer | Mathematically shortest | Depends on terms and discipline |
Investing Fundamentals: Growing Your Wealth
Investing is how you put your money to work, allowing it to grow beyond what’s possible through saving alone. Understanding basic investment concepts is essential for anyone looking to build wealth over time and achieve “long-term financial security”.
- Start investing as early as possible to benefit from compound growth
- Diversify across different types of investments
- Consider your time horizon and risk tolerance
- Keep investment costs low through index funds or ETFs
The power of compound interest makes investing early one of the most impactful financial decisions you can make. A 25-year-old who invests $5,000 annually until age 65 can accumulate over $1 million with an 8% average annual return, while waiting until age 35 to start the same investment plan results in less than half that amount. This dramatic difference illustrates why time in the market is more important than timing the market.
 4.8Excellent
4.8ExcellentTop Investment Platform: Fidelity Investments
Fidelity offers a comprehensive platform suitable for both beginning and advanced investors. With no account minimums, zero commission trades on stocks and ETFs, excellent research tools, and outstanding customer service, Fidelity provides exceptional value for investors at all levels.
Without a basic understanding of investment principles, many people make costly mistakes such as panic selling during market downturns or chasing performance by investing in whatever has recently performed well.
Modern portfolio theory emphasizes diversification across different asset classes. This strategy helps manage risk by ensuring that your investments don’t all move in the same direction simultaneously, providing more stable returns over time and protecting against catastrophic losses in any single investment.
Tax-advantaged investment accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs offer significant benefits that can dramatically increase your long-term returns. The combination of tax deductions, tax-deferred growth, and potential employer matching in retirement accounts makes them the ideal starting place for most investors before considering taxable investment accounts.
Retirement Planning: Securing Your Future
Retirement planning is perhaps the longest financial project most people will undertake, spanning decades of saving and investing to ensure financial security in later life.
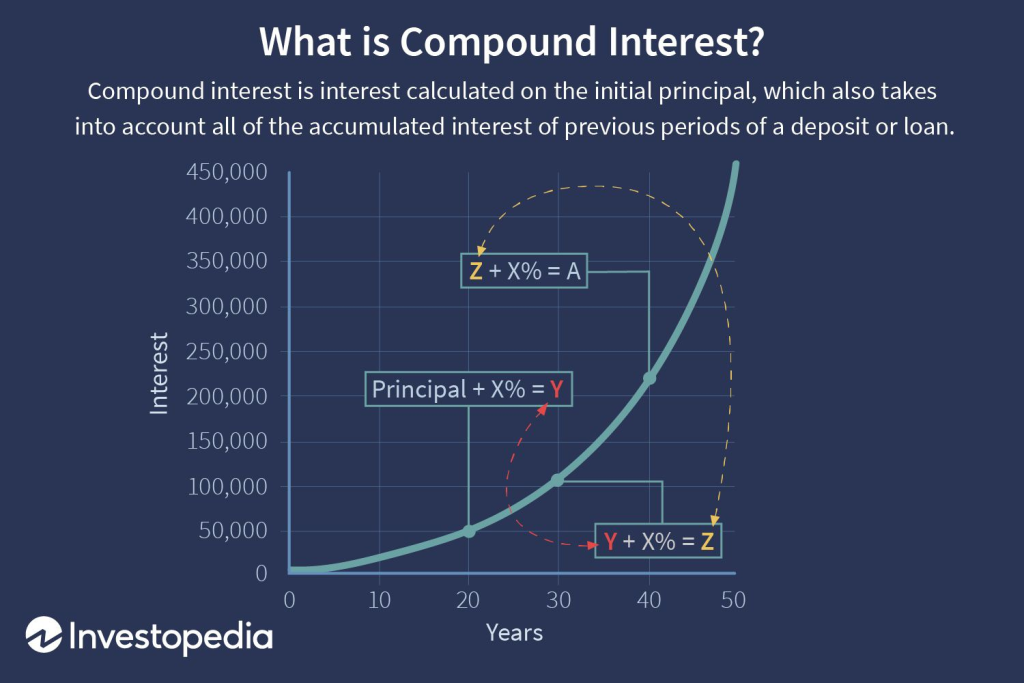
The changing landscape of retirement in America has shifted responsibility from employers to individuals. With traditional pensions increasingly rare, mastering “personal retirement planning” has become essential for avoiding financial hardship in your later years.
Understanding your retirement number—the amount you need to save—requires projecting your future expenses and income sources. Financial advisors often suggest aiming to replace 70-80% of your pre-retirement income, though this varies based on your expected lifestyle, healthcare needs, and other personal factors.
The sequence of returns risk—the danger of experiencing poor investment performance early in retirement—can dramatically impact how long your savings last. Strategies to mitigate this risk include maintaining a more conservative asset allocation, establishing a cash buffer for initial retirement years, or implementing a “bucket strategy” that segments your investments based on when you’ll need them.
Insurance: Protecting Your Financial Life
Insurance forms a crucial part of your financial foundation by protecting against catastrophic risks that could otherwise destroy your financial security.

Health insurance is non-negotiable in a sound financial plan. Medical emergencies represent one of the leading causes of bankruptcy in America, making adequate health coverage essential for protecting your finances from potentially ruinous healthcare costs. When selecting a policy, carefully balance premiums against deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums based on your health needs and financial situation.
Life insurance becomes essential when others depend on your income. Term life insurance provides pure death benefit protection at affordable rates, making it the appropriate choice for most families. The coverage amount should account for replacing lost income, paying off debts, and funding future goals like education expenses.
Property and casualty insurance protects your valuable assets from damage or loss. Homeowners or renters insurance, auto insurance, and umbrella liability policies form the backbone of this protection. Review coverage limits regularly to ensure they keep pace with rising replacement costs and your changing asset picture.
Tax Planning: Keeping More of What You Earn
Strategic tax planning is a critical yet often overlooked component of personal finance. Effective tax management can significantly increase your lifetime wealth by reducing one of your largest expenses.
Tax-loss harvesting—selling investments at a loss to offset capital gains—can reduce your tax bill while maintaining your overall investment strategy. This technique works by replacing the sold investment with a similar (but not identical) one to maintain market exposure while capturing the tax benefit of the loss.
Understanding “tax-advantaged accounts” and their optimal use can dramatically impact your long-term wealth. The strategic decision between traditional (pre-tax) and Roth (after-tax) retirement accounts should consider your current tax bracket versus your expected tax situation in retirement, creating opportunities for “tax diversification” that provides flexibility in retirement withdrawal strategies.
Gift and estate tax planning becomes increasingly important as your wealth grows. Current tax laws allow substantial lifetime gift and estate tax exemptions, but these provisions may change over time, making it important to stay informed about legislative developments that could affect your legacy planning.
Financial Technology: Tools for Better Money Management
Financial technology has revolutionized personal finance management, making sophisticated tools and services accessible to everyone.
Automated saving and investing apps like Acorns, Digit, and Qapital use behavioral psychology principles to make saving effortless. These tools can round up purchases, analyze spending patterns for safe withdrawal amounts, or implement rules-based savings that gradually build your financial cushion without requiring constant attention.
Comprehensive financial dashboard apps provide unprecedented visibility into your complete financial picture. Services like Personal Capital, Mint, and YNAB aggregate information from all your financial accounts, providing insights and analytics that were previously available only to those with financial advisors or significant technical skills.
The rise of robo-advisors has democratized investment management, offering algorithm-driven portfolio construction and management at a fraction of traditional advisor costs. These services like Betterment, Wealthfront, and Vanguard Digital Advisor can provide sophisticated investment strategies including tax-loss harvesting, automatic rebalancing, and globally diversified portfolios with minimal human intervention.
Teaching Children About Money: Building Financial Literacy Early
Financial education often begins at home, and teaching children sound money management principles can give them a significant advantage throughout their lives.

Age-appropriate money lessons help children develop healthy financial habits. For young children, concepts like saving, delayed gratification, and distinguishing between needs and wants form the foundation. Older children can learn about budgeting, compound interest, and even basic investing principles through “hands-on activities” and real-world practice.
Allowance systems offer practical financial experience in a controlled environment. Whether tied to chores or provided unconditionally, allowances help children practice making spending decisions, setting savings goals, and experiencing natural consequences of their choices while the stakes remain low.
Involving children in family financial discussions—at an appropriate level—helps demystify money management. Explaining why you comparison shop, how you budget for vacations, or how you evaluate value can provide valuable context that shapes their future approach to financial decisions.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Financial Future
Personal finance is ultimately about aligning your money with your values and goals. The principles and strategies outlined in this guide provide a framework for making informed financial decisions that support your unique vision for the future.
Provide distinct approaches for different financial personalities, such as automatic systems for those who prefer not to think about money regularly, or detailed tracking for those who gain satisfaction from optimization. The best personal finance system is one that you’ll actually maintain consistently over time.
Personal finance is not about perfection but progress. Small, consistent improvements in how you manage money can compound dramatically over time, creating financial security and opportunities that might otherwise remain out of reach. By applying the fundamentals covered in this guide, you can take control of your financial future and build a life aligned with your deepest values and highest aspirations.




